Did you know that some of the words we use every day, like algebra, coffee, and sugar, actually come from Arabic?
The Arabic language is built on a clever root system, where just three letters can give rise to dozens of related words. This didn’t happen overnight; it evolved over centuries, shaping the language we know today. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the Arabic language origin tree, explore the fascinating roots behind familiar words, and discover how this ancient system quietly influences the way we speak even now.
History of the Arabic Language
Did you know that Arabic started in the Arabian Peninsula, where early Arab tribes spoke many different dialects? Over time, these dialects gradually came together, forming what we now know as the Arabic language.
The oldest Arabic writings go back to around the 4th century CE, but people were speaking Arabic long before it was written down. A huge turning point happened in the 7th century CE with the revelation of the Qur’an, as it preserved Arabic in a clear, powerful, and standardized form, making it easier for people across generations to understand and use.
Because of this, Arabic has remained strong, consistent, and widely understandable for centuries, and you can tap into this rich history as you learn the language.
The Position of Arabic in the Afro-Asiatic Language Family
Arabic belongs to the Afro-Asiatic language family, one of the oldest language families in the world, spoken across the Middle East and North Africa. Within this family, Arabic belongs to the Semitic branch and is classified as a Central Semitic language.
Other well-known Semitic languages include:
- Hebrew
- Aramaic
- Amharic
These languages share common features such as root-based words and similar grammar rules. This shared structure explains why Arabic feels closely connected to other ancient languages.
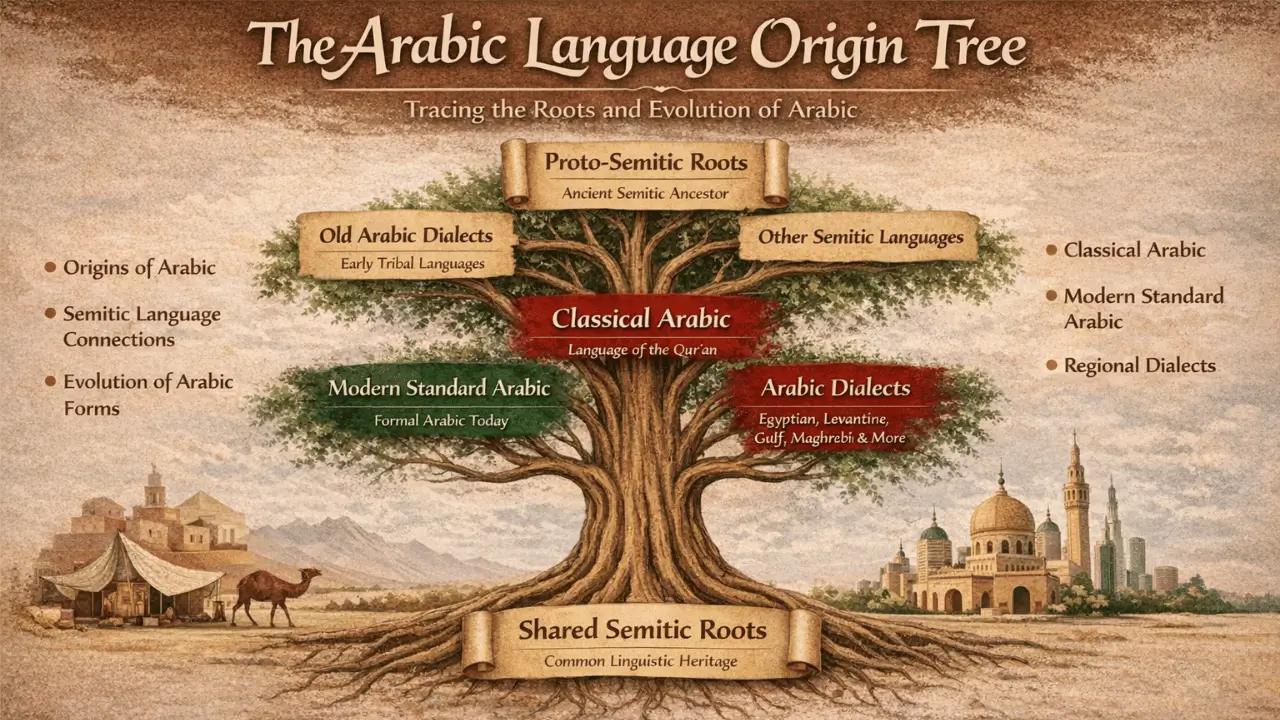
What Is the Arabic Language Origin Tree?
The Arabic language origin tree is a simple way to understand where Arabic comes from and how it developed over time. Think of it like a family tree; it shows Arabic’s roots, its close relatives, and how different forms of the language grew and branched out through history.
By looking at the Arabic language tree, you can easily see:
- Where Arabic originally came from
- How is it related to other Semitic languages
- How Classical Arabic and modern forms of Arabic evolved
This perspective makes the history of Arabic easier to understand and more interesting, especially for learners who want to know why the language is structured the way it is.
Key Components of the Arabic Language Tree
After explaining the Arabic Language Origin Tree, let’s discuss the key components of the Arabic Language Tree:
- Proto-Semitic roots: Ancient ancestor of all Semitic languages
- Old Arabic dialects: Spoken by pre-Islamic tribes
- Classical Arabic: Standardized through the Qur’an
- Modern Standard Arabic: Used today in formal contexts
- Arabic dialects: Egyptian, Levantine, Gulf, Maghrebi, and others
Despite dialect differences, all forms connect back to the same linguistic roots.
Classical Arabic vs. Modern Standard Arabic
Arabic exists in multiple forms, but the two most important are:
Classical Arabic
- The language of the Qur’an
- Used in classical Islamic texts, poetry, and early literature
- Preserved with strict grammatical rules and timeless expressions.
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA)
- A modernized form of Classical Arabic
- Used in news, books, education, and formal communication
- Widely understood across the Arab world
While MSA adapts to contemporary needs, it remains deeply rooted in Classical Arabic, giving learners a strong linguistic foundation.
At Mubark Academy, we provide structured courses that bridge Classical Arabic and MSA, helping students read, write, and communicate confidently in both forms.
Enroll at Mubark Academy Today

How Arabic Spread Across the World
At Mubarak Academy, students learn not only how to speak Arabic, but also how the language spread and shaped civilizations across the globe.
Arabic expanded through several key factors:
- Islam: The Qur’an made Arabic sacred and widely learned
- Trade: Arab merchants traveled across continents
- Islamic empires: Arabic became the administrative and scholarly language
Today, Arabic is spoken across:
- The Middle East
- North Africa
- Parts of East Africa
- Muslim communities worldwide
Read Also: Importance of Studying Arabic Language
How Arabic Influenced Other Languages
Arabic has had a massive influence on many languages due to trade, science, and Islamic civilization. Thousands of words in other languages come from Arabic.
Examples include:
- English: algebra, sugar, coffee, alcohol
- Spanish: azúcar, almohada, aceite
- Turkish, Persian, Urdu: more than 20% of everyday vocabulary in some contexts comes from Arabic
During the Islamic Golden Age (8th–14th century), Arabic was the language of science, medicine, mathematics, and philosophy, which helped spread its words and concepts far beyond the Arab world.
In fact, about 30% of Spanish and Portuguese scientific and scholarly terms trace back to Arabic.
Start Learning Arabic from Its Roots
Want to understand Arabic from its roots and unlock the meanings behind these words?
Join Mubarak Academy’s Arabic Language Course and learn Classical and Modern Arabic with qualified teachers, structured lessons, and authentic learning methods.
Conclusion
The Arabic language is not just a means of communication; it is a living history. From its Afro-Asiatic roots to its global influence, Arabic has shaped civilizations, preserved sacred texts, and enriched countless languages. Understanding the Arabic language origin tree gives us a deeper appreciation of its strength, beauty, and lasting legacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How old is the Arabic language?
Arabic is over 1,500 years old in written form, but its spoken roots go back several thousand years. Early forms of Arabic existed long before Islam, while Classical Arabic was firmly established in the 7th century CE.
2. Can understanding the Arabic origin tree help me learn the language?
Yes! Recognizing root patterns makes it easier to understand new words, expand your vocabulary, and see the connections between different words.
3. Are all English words from Arabic related to science or food?
No. While many come from science, math, or trade (like algebra or saffron), others are everyday items or concepts, including terms in art, culture, and daily life.




