Over 1.8 billion Muslims recite the Qur’an in Classical Arabic, while Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is used daily by millions for news, education, and official communication. Even though both forms look similar, they are used in very different contexts. This guide explains Classical Arabic vs Modern Standard Arabic and helps you choose the right one for your goals.
What Is Classical Arabic?
Classical Arabic is the prestigious, standardized form of Arabic associated with the Qur’an and much of pre-modern Arabic scholarship and literature. In practice, when students say “I want to learn Classical Arabic,” they usually mean gaining enough Arabic to confidently understand Qur’anic vocabulary, classical texts, and traditional Islamic studies, rather than everyday conversation.
It’s also worth knowing that many people loosely call both Classical Arabic and MSA “al-fuṣḥā,” because they share the same high-status “standard” feeling compared to everyday dialects.
Read Also: How to Learn Classical Arabic Language
What Is Modern Standard Arabic (MSA)?
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is the standardized form of Arabic used across the Arab world in formal writing and formal speech. You’ll see it in newspapers, books, and official documents, and you’ll hear it in news broadcasts and prepared speeches.
Within the Arabic language Origin Tree, MSA is historically rooted in Classical Arabic. Most linguistic references describe it as very close to Classical Arabic, with differences appearing mainly in style and modern vocabulary. This shared foundation is why many learners notice that improving their MSA also helps them understand Classical Arabic texts more easily, especially when reading or studying grammar.
Classical Arabic vs Modern Standard Arabic
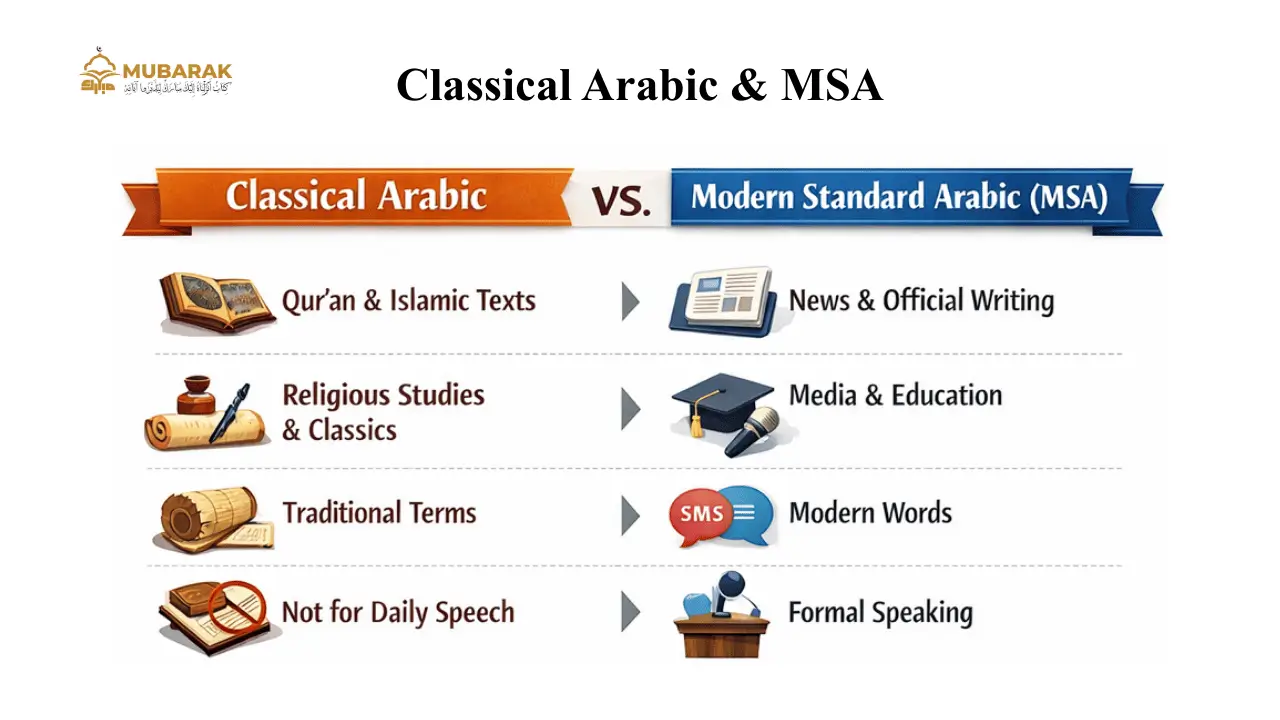
If you’re comparing Modern Standard Arabic vs Classical Arabic, understanding the key differences can help you decide which one best fits your learning goals:
1. Purpose:
- Classical Arabic: Your gateway to the Qur’an and classical Islamic texts
- MSA: Your gateway to modern formal content, such as news and official writing
2. Usage:
- Classical Arabic: Qur’an, Islamic studies, classical literature
- MSA: News, education, formal communication
3. Vocabulary
- Classical Arabic: Traditional and classical terms
- MSA: Includes modern words and expressions
4. Spoken Use
- Classical Arabic: Not used in daily conversation
- MSA: Used in formal speaking, not everyday dialects
Which One Should You Learn?
If your goal is to understand the Qur’an and classical Islamic texts, Classical Arabic is essential. If you want to read news, follow the media, or study Arabic formally, MSA is more practical.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take to Become Fluent in Arabic?
Grammar Differences Between Classical and Modern Arabic
At the grammar level, Classical Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) are far more similar than different. In fact, they share the same core grammatical system. However, some differences appear in usage, flexibility, and frequency, especially in modern contexts.
1. Core Grammar Rules
Both Classical Arabic and MSA follow the same foundational rules, including:
- Noun cases (rafʿ, naṣb, jarr)
- Verb conjugation patterns
- Gender and number agreement
- Sentence structures (nominal and verbal sentences)
This means that learning grammar in one form directly supports the learning of the other.
2. Case Endings (Iʿrāb)
Both forms include case endings (iʿrāb) in the grammar tradition, but many students feel them more strongly in Qur’anic/classical study because teachers and books often emphasize precision and detailed analysis. In many MSA resources, the focus starts with comprehension and clean sentence building, then moves into deeper grammar details over time.
3. Sentence Length and Style
- Classical Arabic: Tends to use longer, more complex sentence structures with rich rhetorical styles.
- MSA: Prefers clearer, shorter sentences suited to journalism, education, and formal communication.
4. Use of Particles and Expressions
- Classical Arabic: Uses a wider range of classical particles and connectors that may feel unfamiliar to modern learners.
- MSA: Uses a more limited, standardized set of particles for clarity and consistency.
5. Verb Usage
- Classical Arabic: Frequently uses advanced verb forms, passive constructions, and stylistic shifts.
- MSA: Uses the same verb system but favors simpler, more direct verb choices.
There is no separate grammar for Classical Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic. The differences lie in how strictly the rules are applied and how often complex structures are used.
Learn Arabic Grammar for Understanding Quran

Learn Classical Arabic Online with Mubarak Academy
If your goal is to understand the Qur’an more directly, the smartest path is to build a strong foundation in standard Arabic (reading skills, morphology, and core grammar), then gradually add Qur’anic vocabulary and classical text practice. This balanced approach bridges Classical Arabic vs Modern Standard Arabic, giving you both linguistic structure and the depth needed for Islamic studies.
At Mubarak Academy, our Arabic Language Course is designed for online learners at every level, offering structured lessons with flexible options such as one-on-one or group classes, guided by qualified instructors.
Book your Trial Class and Begin Classical Arabic
Conclusion
At the end of the day, classical Arabic vs modern standard Arabic is not a battle; it’s a question of the text-world you want to enter first. Classical Arabic is ideal for Qur’anic and traditional texts, while MSA is ideal for modern formal Arabic in writing and media, and the shared foundation means your effort in one usually strengthens the other.
FAQs About Classical Arabic vs Modern Standard Arabic
1. Is Modern Standard Arabic the same as Classical Arabic?
They’re not identical, but they are very close. Major references describe Modern Standard Arabic as differing only slightly from Classical Arabic, mainly in style and vocabulary rather than grammar.
2. If I learn MSA first, will it help me understand the Qur’an?
Yes, especially for reading skills and core grammar. MSA builds a strong foundation, after which you can add Qur’anic vocabulary and classical reading practice for deeper understanding.
3. Do I need Classical Arabic to speak with Arabs today?
For daily conversation, you usually need a spoken dialect. MSA helps with formal contexts, reading, and media, while Classical Arabic is mainly for Qur’anic and classical studies.
4. Do modern Arabs understand Classical Arabic?
Yes, most educated Arabs understand it, especially in the Qur’an, sermons, and formal settings. However, full mastery usually requires study because it’s not used in daily speech.
5. Is MSA based on the Qur’an?
Yes. Modern Standard Arabic comes from Classical Arabic, the language of the Qur’an. The grammar is almost the same, but MSA includes modern vocabulary.
6. What are the three types of Arabic?
• Classical Arabic: Qur’an and classical Islamic texts
• Modern Standard Arabic (MSA): News, books, education
• Spoken Dialects: Everyday speech (Egyptian, Gulf, Levantine, etc.)
7. Should I learn MSA before Egyptian Arabic?
For most learners, yes.
• Learn MSA first for reading, writing, and grammar
• Learn Egyptian Arabic for daily conversation
Best option: MSA first, then Egyptian Arabic.




